The pandemic has shifted people’s shopping behavior towards online resources. Mobile screen-based panoramic virtual reality (VR) appears to be a promising form for future online shopping. However, the existing user interface (UI) design of panoramic VR shopping needs more natural interactions based on a rational standard design guideline. In this article, we first conducted a heuristic study to compare six representative virtual store apps. This revealed a gap between users’ requirements and the current design attempts. Thus, a UI design guideline for panoramic VR in the shopping scene was presented. Then, we conducted a verification study with a demo optimized according to our design guideline. Both user experience and interactive efficiency improved as a result of the design guideline. Our design guidelines and discoveries derived from user studies provided references for the design, development, and potential use of dynamic panoramic VR in shopping scene.
The main contributions of this research are as follows:
(1) identified the shortcoming of the existing design of panoramic VR shopping on mobile;
(2) a comprehensive interface design guideline for panoramic VR shopping on mobile devices was proposed;
(3) instructions for the implementation of the design guideline in practice was provided.
Optimization and user study
To evaluate our design guideline’s effectiveness and gain insights into the potential limitations, we recreated a panoramic VR store from the previous scenario in S2 (see subsection 3.2, the liquor store) following the guideline. The space design and shelf layout in this S2 are more general, like what we daily seen in most shopping malls and stores. Then we conducted a verification user study within target participants.
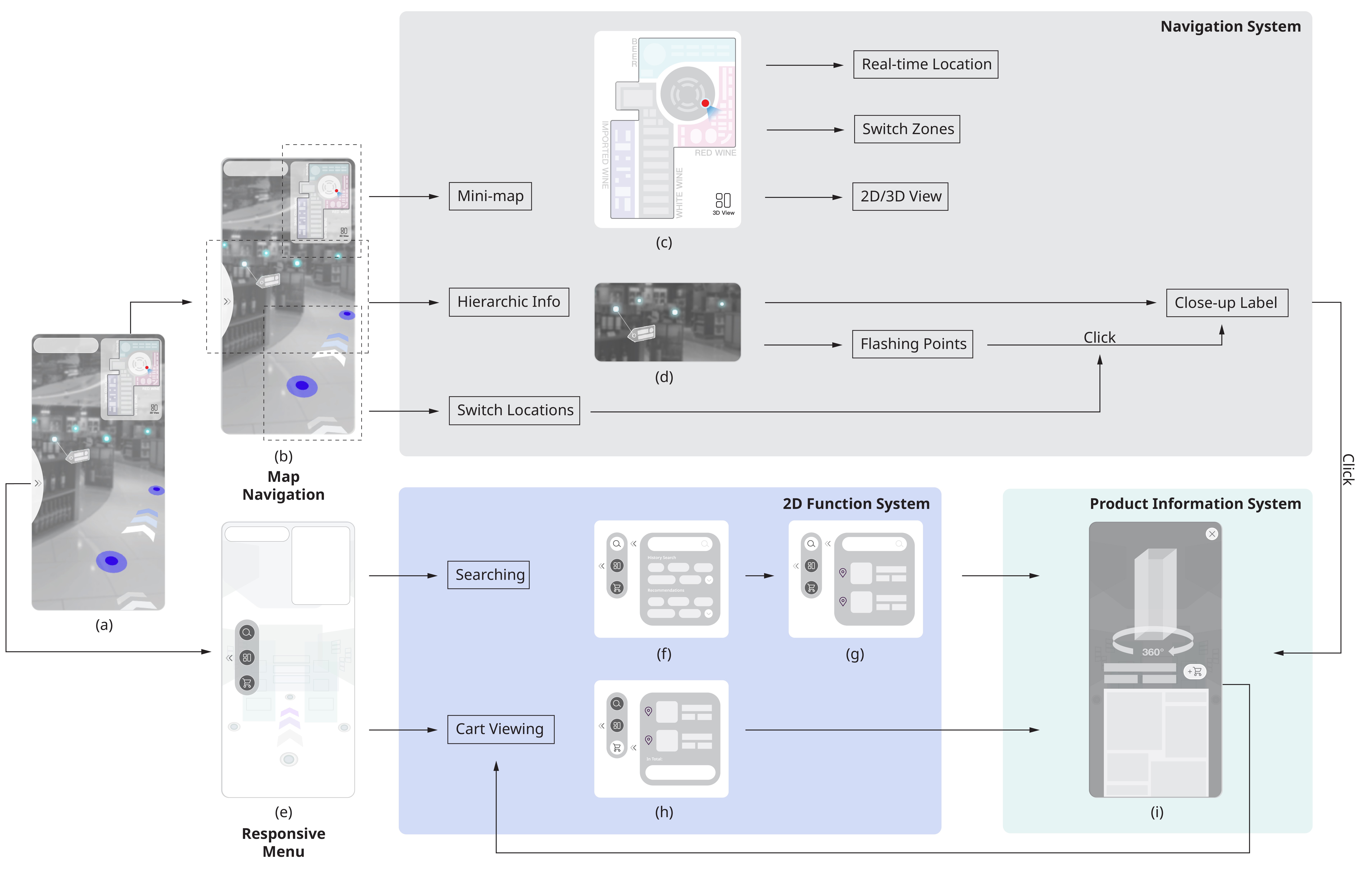
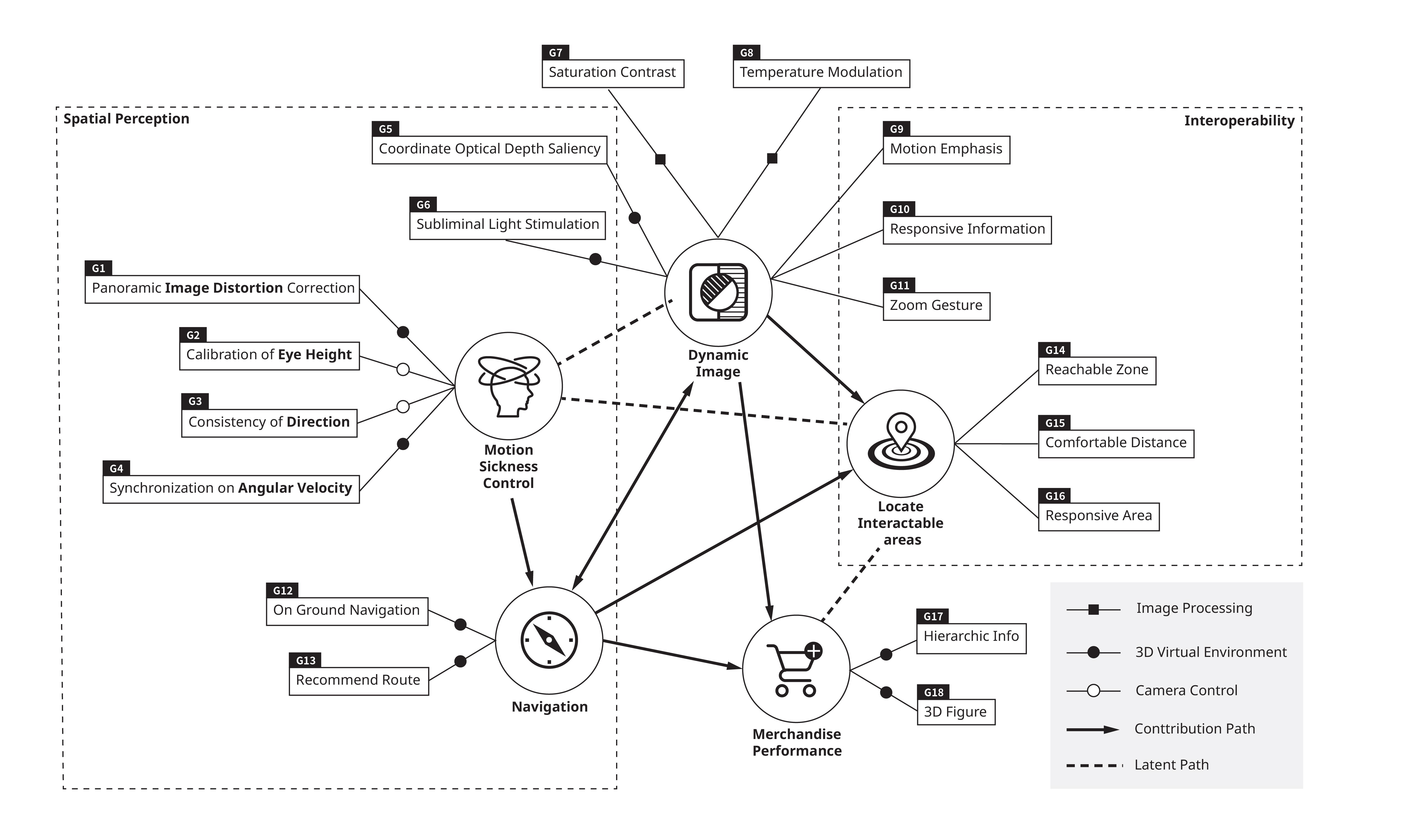
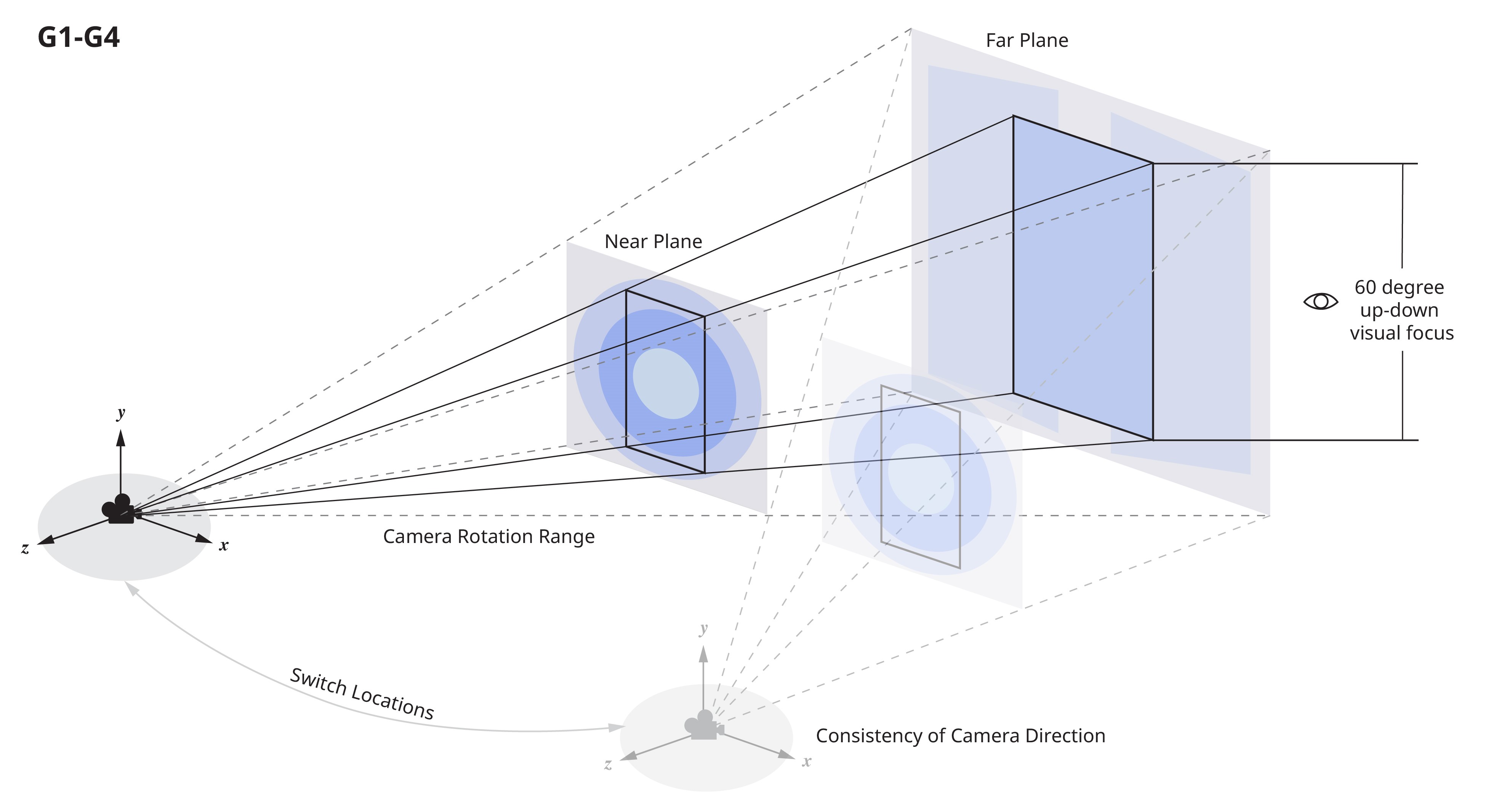
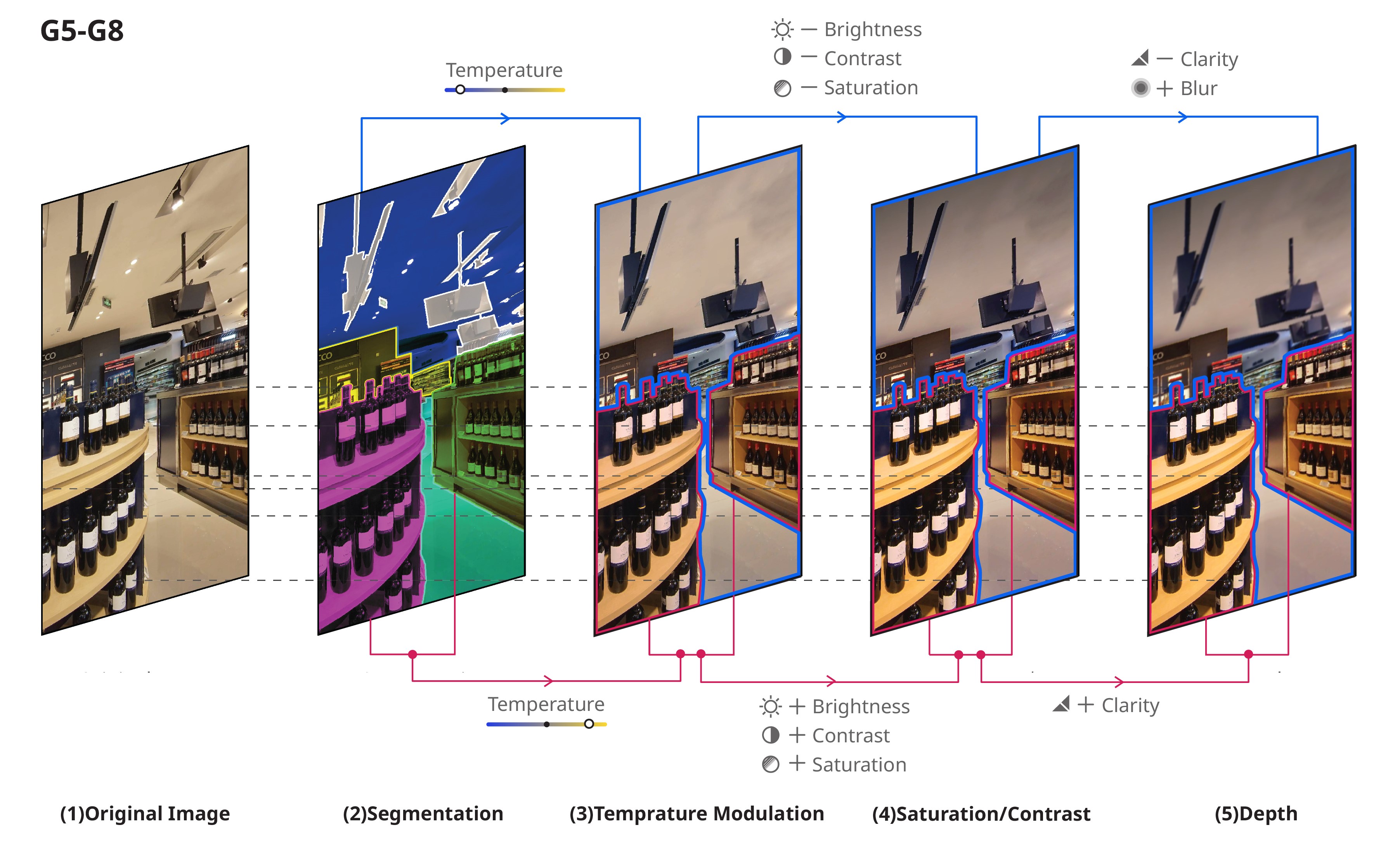
Design standard guideline
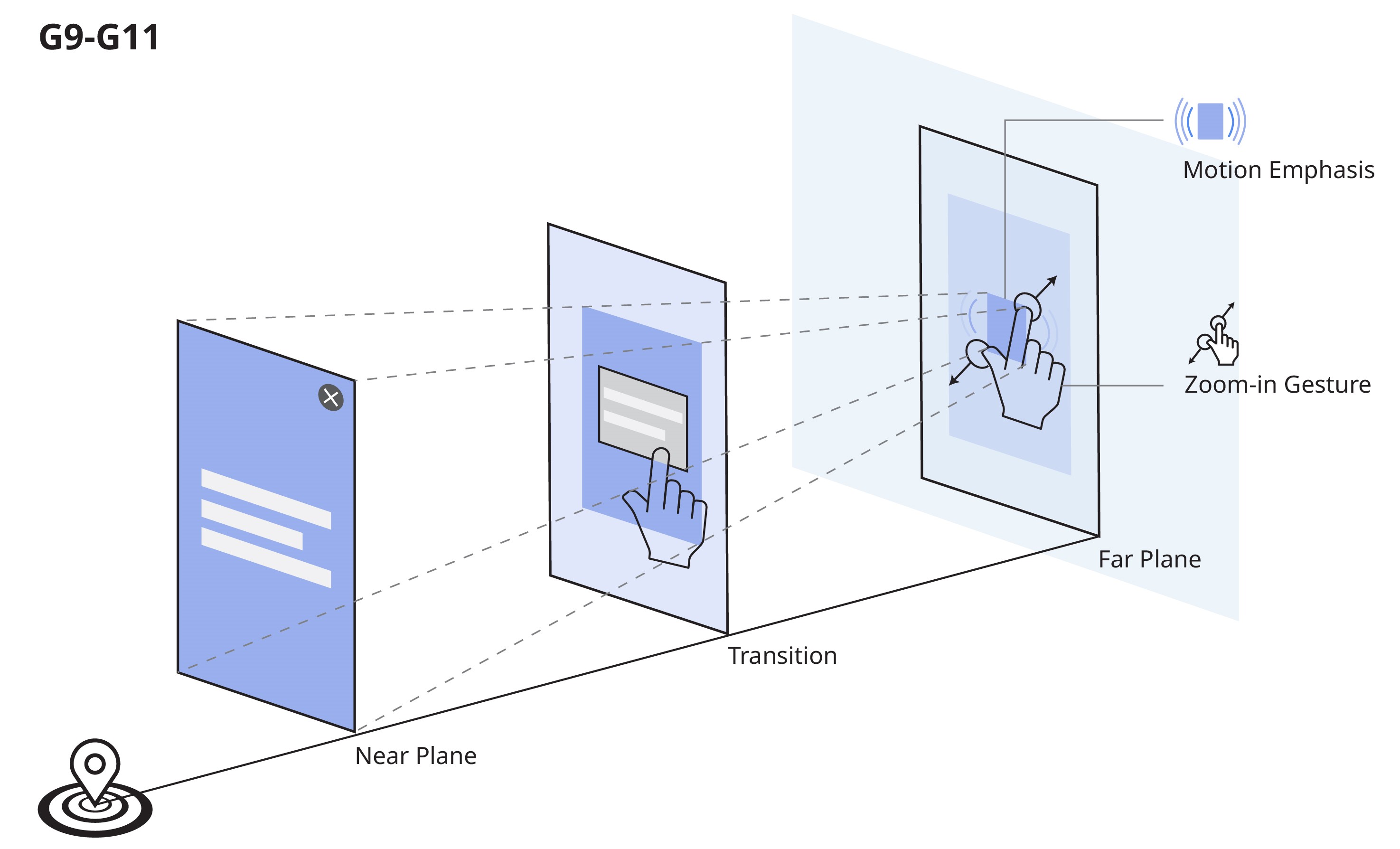
Heuristic study and case study
In order to better comprehend the interaction in the panoramic VR shopping, we selected 6 representative products for analysis. They were JD Panorama, Obsess Online Mall, Qbit 3D Virtual Store, Ke Holdings, Dcar, Bikeconfig. We integrated the first three panoramic shopping platforms, and the rest three were in subdivisions. To evaluate the interaction design of these systems, we invited two professional UI designers to evaluate them with a checklist containing 26 features in 4 aspects, selected from Purdue Usability Testing Questionnaire [27]. The 4 aspects were architecture and navigation, layout and design, content and readability, behavior and interaction (see Table 1. Questions with significant discrepancies are highlighted). Based on the comparison of these platforms and designers’ experiences with them, we derived five attributes that were commonly appeared and urgent to be improved in mobile panoramic shopping.
To verify our thoughts in embryo, we conducted a within-subjects heuristic study with two panoramic VR stores on mobile. After reached with several teams, the Taobao platform agreed to share confidential data and original panoramic images of these two stores with us, in return for sharing our researches. Two experimental stores are a glass store (S1) and a liquor store (S2). S1 is a fashion glasses store inside a two-floor building with an irregular shape of space. S2 is an open-shelf liquor store with five sales zones supermarket-like shelves on one flat floor. Due to the impact of COVID-19, the laboratory and most of the communities closed for quarantine. Thus the experiment was divided into online and offline, following the same procedure. The participants were randomly divided into two groups. The first group experienced S1 and then S2, while the second group did an inverse sequence. The counter-balance can reduce the influence of system familiarity on usability scores. We videotaped the whole experiment better to observe users’ behavior with the consent of participants.